In recent years, the word CRISPR has become widely known. It appears in news stories, documentaries, science books, and even conversations about medicine and technology. But what exactly is it, and why is it generating so much interest?
CRISPR is a tool that allows scientists to modify DNA with great precision. It’s used to correct genetic errors, engineer cells to fight diseases like cancer, and even improve the crops we grow. Although it may sound like science fiction, it’s already being used in labs around the world and has transformed the way genetic research is conducted.
What does CRISPR mean?
CRISPR stands for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats. These special sequences were discovered in bacteria, which use them as a defense mechanism against viruses. When a virus attacks a bacterium, the bacterium can save a fragment of the virus’s DNA as a kind of memory. If the virus attacks again, the bacterium recognizes it and uses an enzyme to cut and destroy it.
Scientists studied this natural system and thought: “If bacteria can cut DNA precisely, could we use this system to edit the DNA of other organisms?” This idea led to the development of CRISPR as a genetic editing tool.

How does CRISPR work?
CRISPR works with two main components that function together:
- A guide RNA, which acts like a GPS to find the exact location in the DNA where a change is needed.
- An enzyme called Cas9, which acts like molecular scissors that cut the DNA at the targeted point.
Once the DNA is cut, scientists can delete, change, or insert specific sequences. For example, they can remove a gene that causes a disease or insert a new one that functions better. This enables highly accurate edits to the genome of any organism.
What makes CRISPR special is that it’s faster, cheaper, and more precise than previous genetic editing techniques. It can also be applied to many types of cells and organisms, from bacteria to humans.
What is CRISPR used for?
CRISPR is already being used in several areas of science and technology:
- Health: It is being explored for treating genetic diseases like sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, and certain types of inherited blindness. It's also being studied for fighting infectious diseases like HIV.
- Cancer: Researchers are testing it to modify immune cells so they can better recognize and destroy cancer cells.
- Agriculture: CRISPR helps develop crops that are more resistant to disease, drought, or climate changes. It can also improve the shelf life or taste of fruits and vegetables.
- Science: It allows researchers to study the function of specific genes, understand how genetic changes affect organisms, and explore new ways to prevent or treat diseases.
In the future, it could even be used to eliminate genes that cause allergies or to manufacture drugs directly inside the human body.
Concerns and debates
Although this gene editing technology is very promising, it also raises important questions:
- Is it ethical to change a baby’s DNA before birth?
- What if these changes are passed on to future generations?
- Could this technology be used to create "enhancements" in healthy individuals?
- Who decides how and when this technology can be used?
These questions concern not only scientists, but also governments, international organizations, and society at large. The decisions made today could have lasting consequences, so it’s essential that CRISPR is used responsibly and under proper regulation.
The future of CRISPR
CRISPR is improving every day to become safer and more precise. In the future, it may help cure currently untreatable diseases, prevent genetic disorders before they appear, and even help stop pandemics.
It’s also being combined with other technologies like artificial intelligence, which helps identify the right genes faster, or nanotechnology, which could improve how the editing system is delivered into the body
In addition, CRISPR is expected to play a key role in personalized medicine, enabling treatments tailored to each patient, with higher effectiveness and fewer side effects. This could fundamentally change how we approach health and medicine.
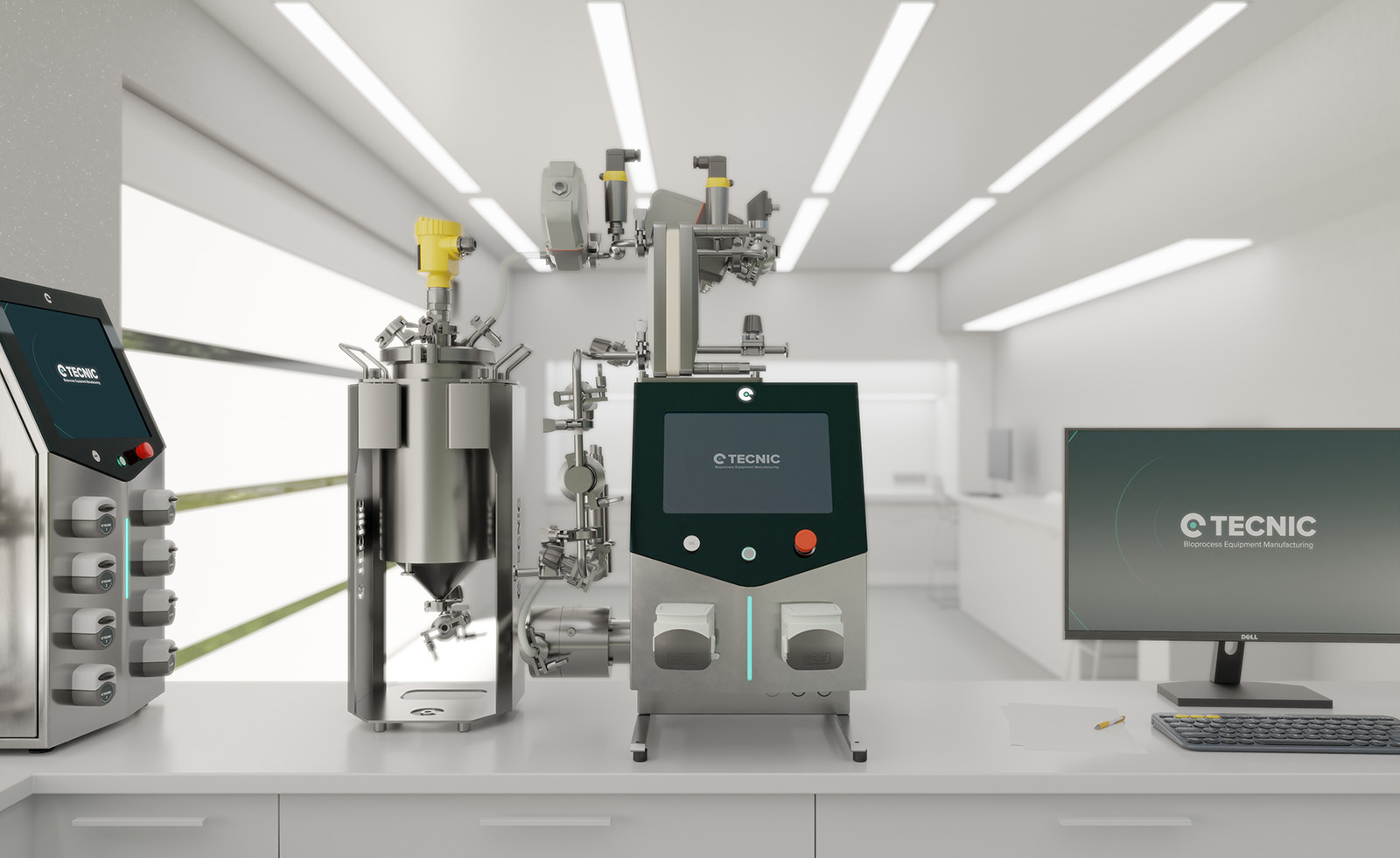
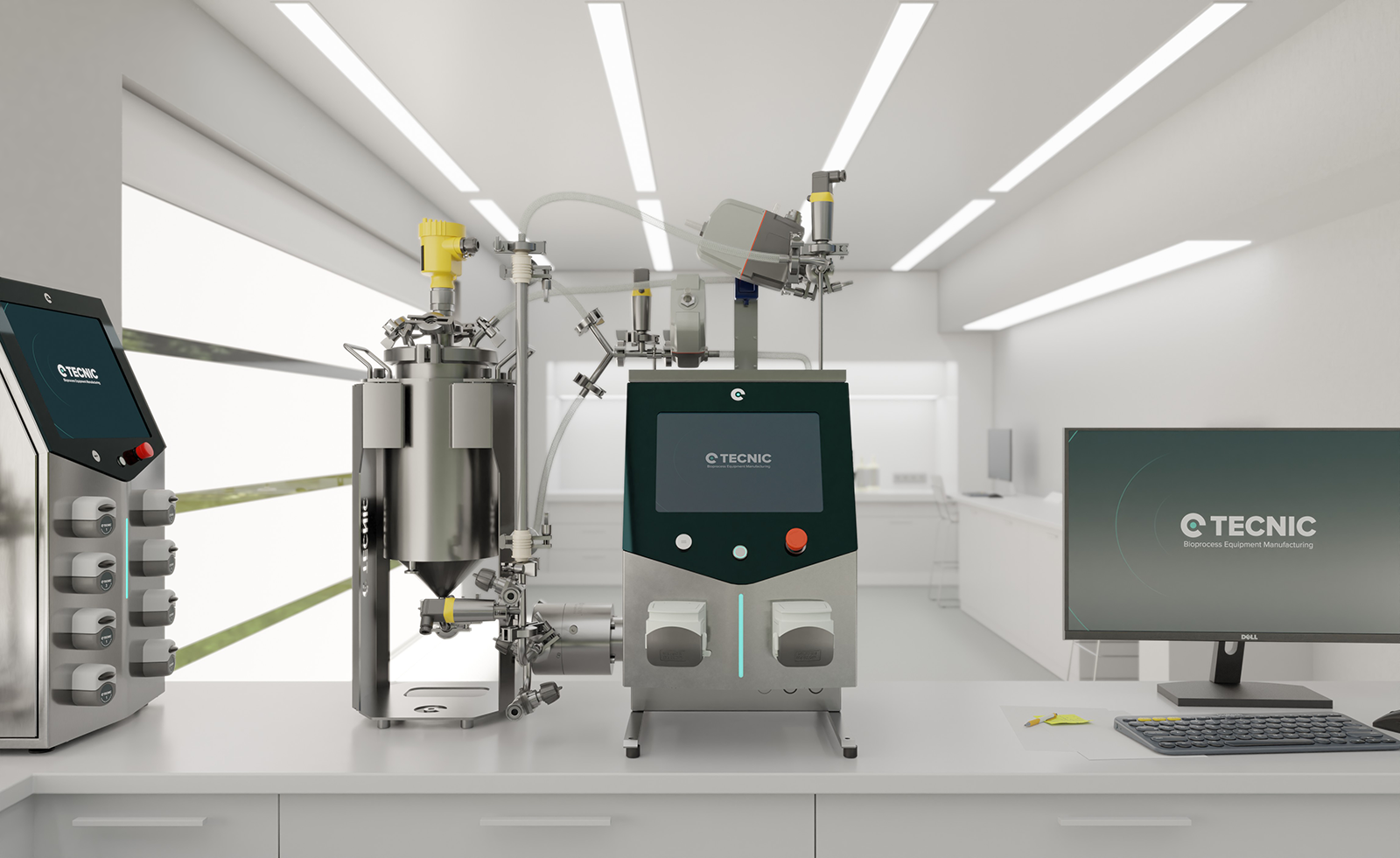
Companies like TECNIC are developing solutions that apply these technologies safely, using advanced equipment and platforms that automate processes, ensure quality, and meet pharmaceutical industry regulations.
Conclusion
CRISPR is a powerful tool that is transforming how we understand and treat many diseases. It allows us to edit DNA with precision, opening new doors in medicine, agriculture, and research. It’s a technology that could improve the quality of life for millions of people around the world.
At TECNIC, we support these advances and work to ensure the technology is applied safely, responsibly, and efficiently. Our mission is to provide solutions that help labs, hospitals, and companies harness the potential of CRISPR in a fast, secure, and science-driven way.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
It’s used to edit DNA, treat diseases, improve crops, and advance genetic research.
It was first identified in bacteria. Scientists like Emmanuelle Charpentier and Jennifer Doudna adapted it for gene editing.
It’s faster, cheaper, and more accurate than earlier methods like TALENs or ZFNs.
It works on many, but editing efficiency and safety depend on the cell type and method used.
Cas9 is an enzyme that cuts the DNA at a specific spot chosen by the guide RNA.